Determinants of community composition in aquatic ecosystems
- Salinity
- Light penetration
- Dissolved oxygen
- Nutrients
- Temperature
- pH
- Flow
Types of marine organisms
- Plankton
- Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton
- Nekton
- Benthos
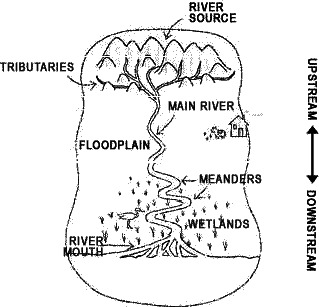
Rivers
Threats to rivers
- Non-point-source pollution
- Siltation
- Dam
Freshwater lakes
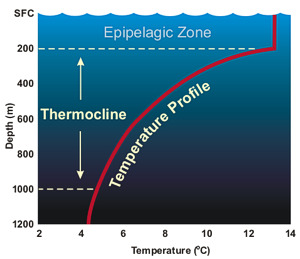
Thermal stratification
Threats to lakes
- Rivers tend to flow into lakes
- Water withdrawals
Wetlands
- ``[S]hallow ecosystems in which the land surface is saturated or submerged at least part of the year''
- Contain vegetation adapted to grow in these saturated environments
- Legal definition is critical due to disproportionate importance of wetlands
Types of wetlands
- Swamp
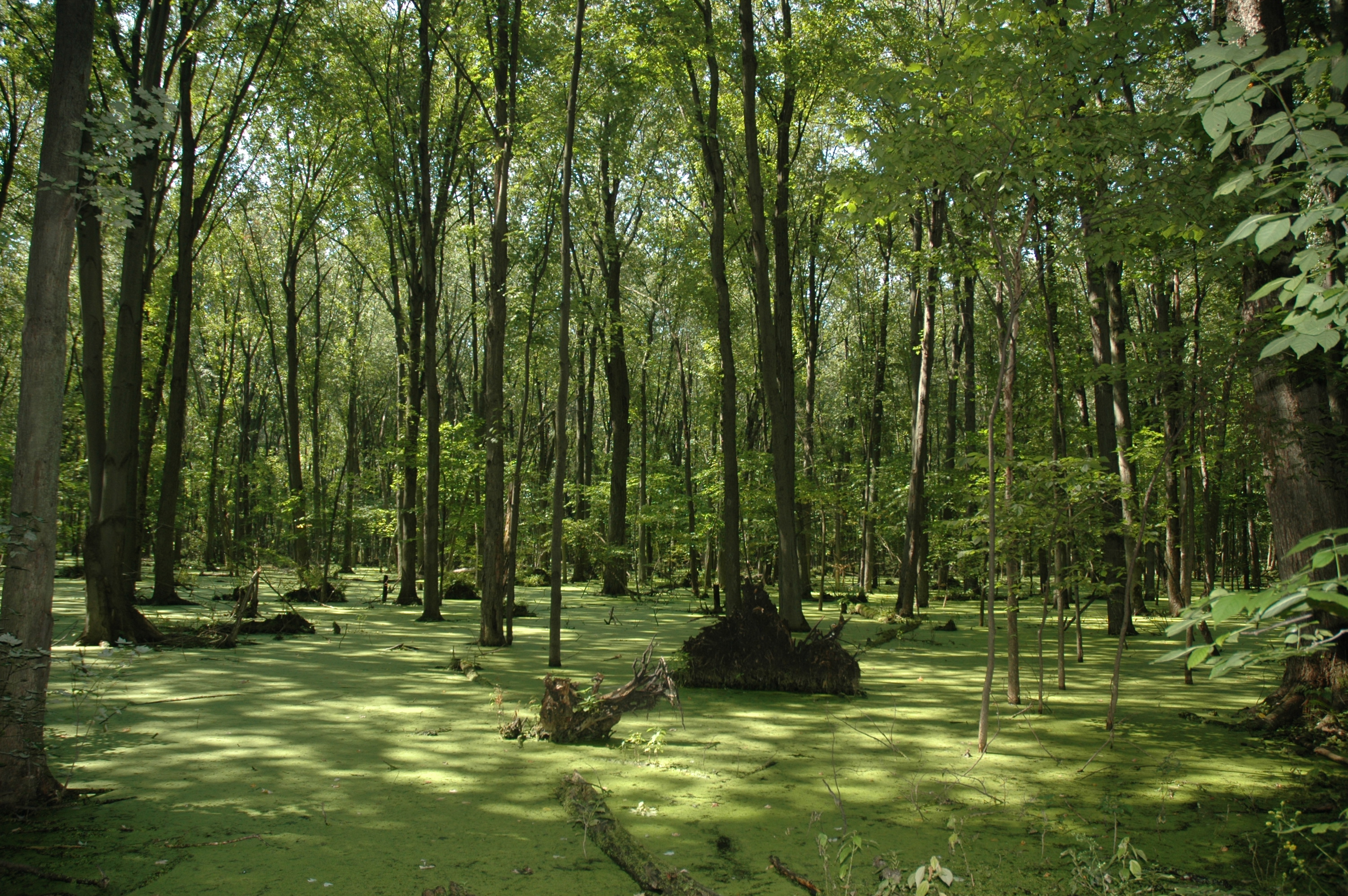
- (Forested wetland) Wetlands dominated by trees; high biological productivity; high nutrient levels
- Marsh
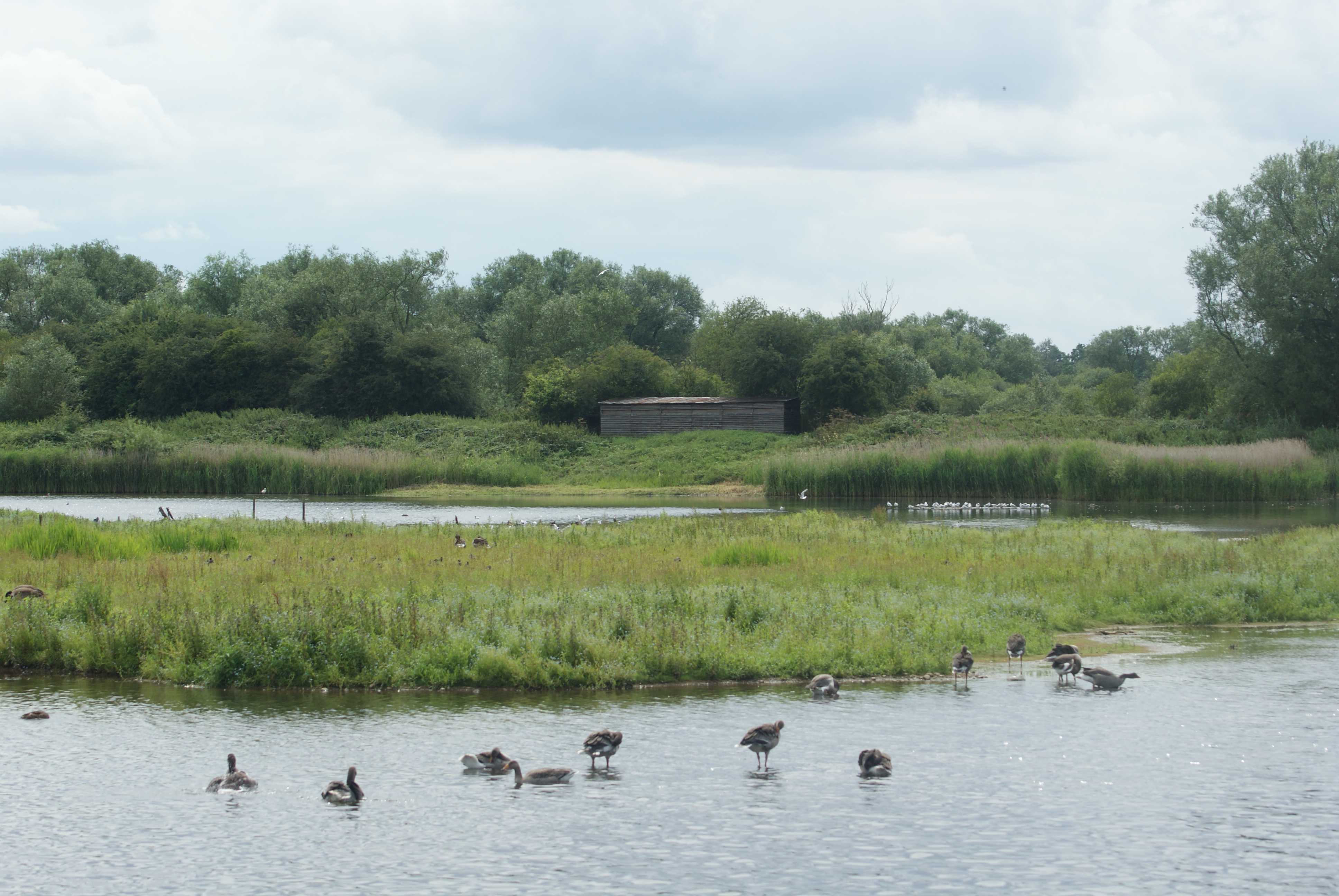
- Wetland dominated by grasses and other vegetation; high biological productivity; high nutrient levels
- Bog
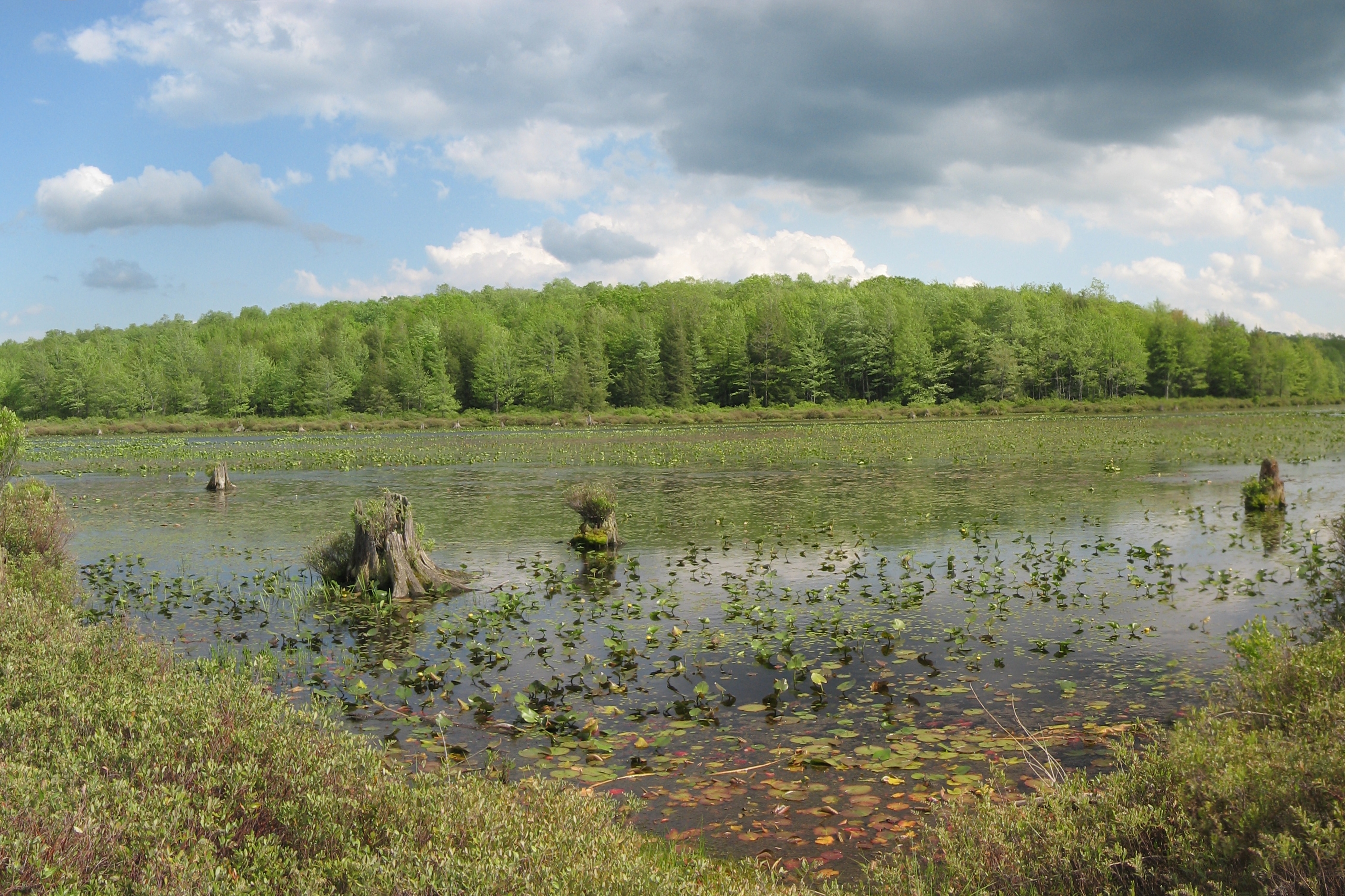
- Area of water-saturated ground, fed by precipitation; containing layers of undecayed vegetation (peat); low biological productivity; low nutrient levels
- Fen
- Area similar to bog, but fed by groundwater
Forested wetland
Marsh
Bog
Threats to wetlands
- Urban sprawl
- Development
- Agriculture
- Pollution
- Pest eradication
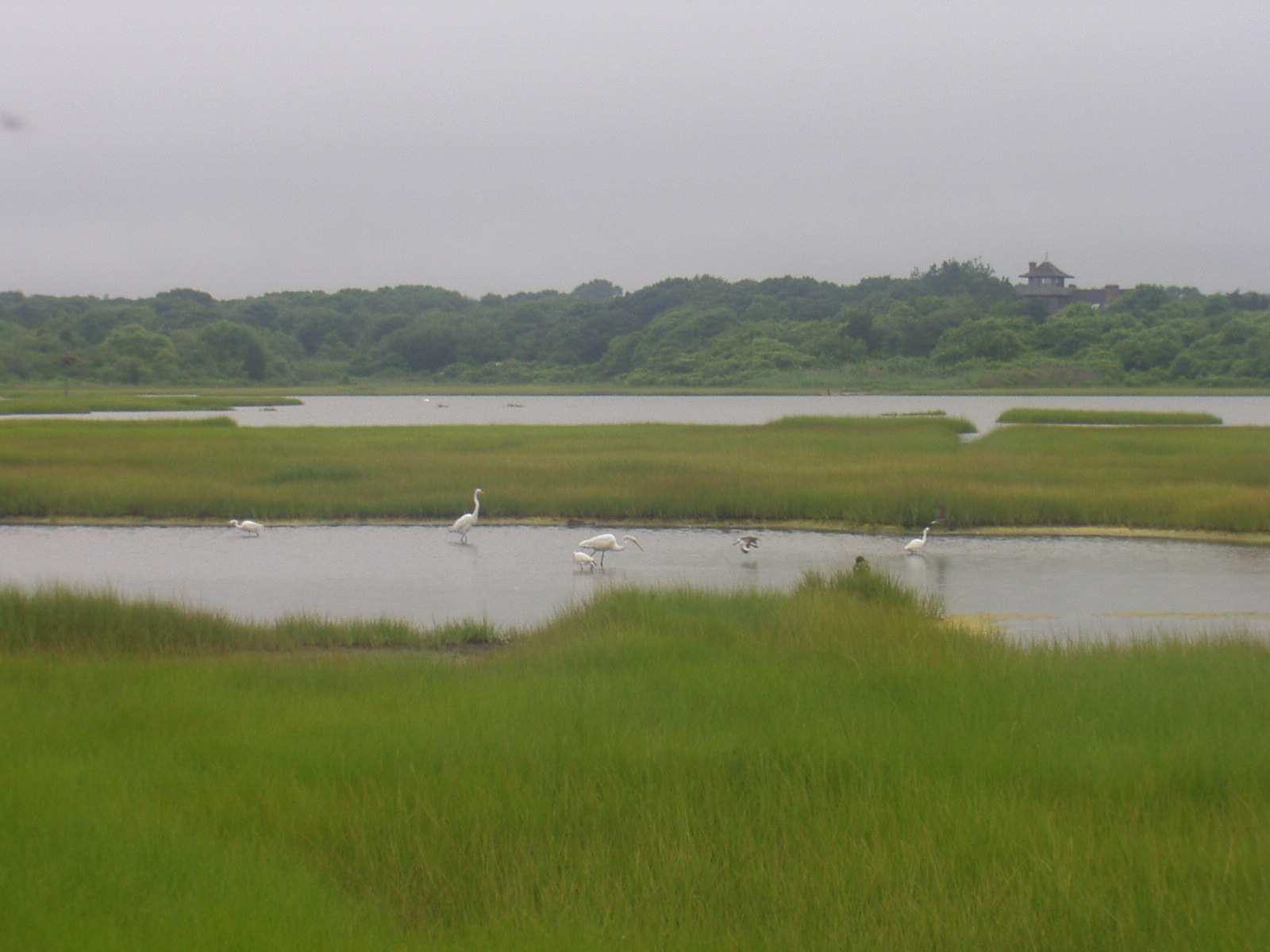
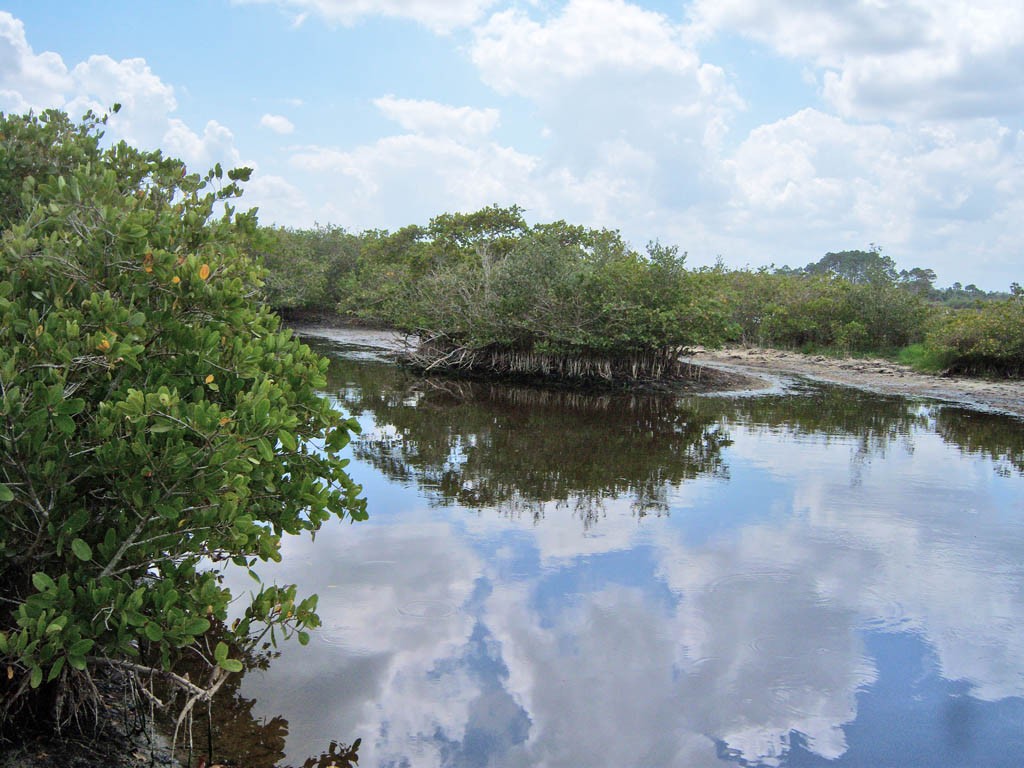
Estuaries
- Combination of factors place them among the most fertile ecosystems:
- Rivers carry terrestrial nutrients into the estuary
- Tidal action promotes rapid nutrient cycling and waste removal
- Significant light penetration into shallow water
- Numerous plants act as primary producers and trap detritus
- Critical habitats for fish and other organisms
Salt marsh
Mangrove forest
Threats to estuaries
- Coastal development
- Pollution
- Aquaculture
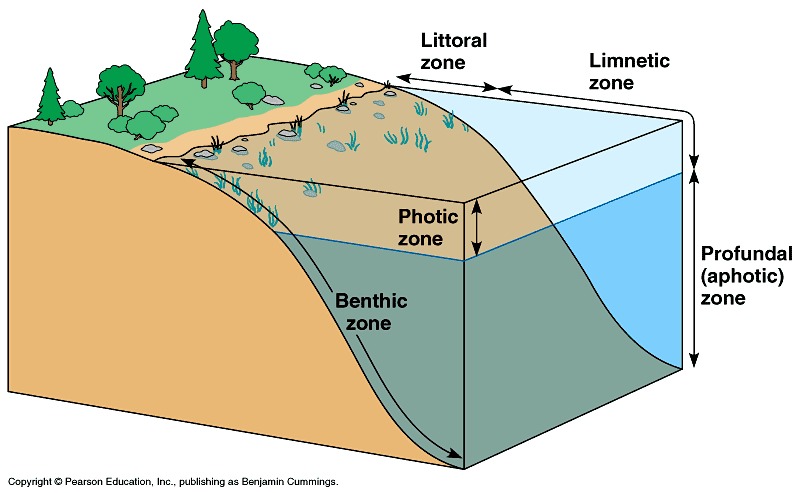
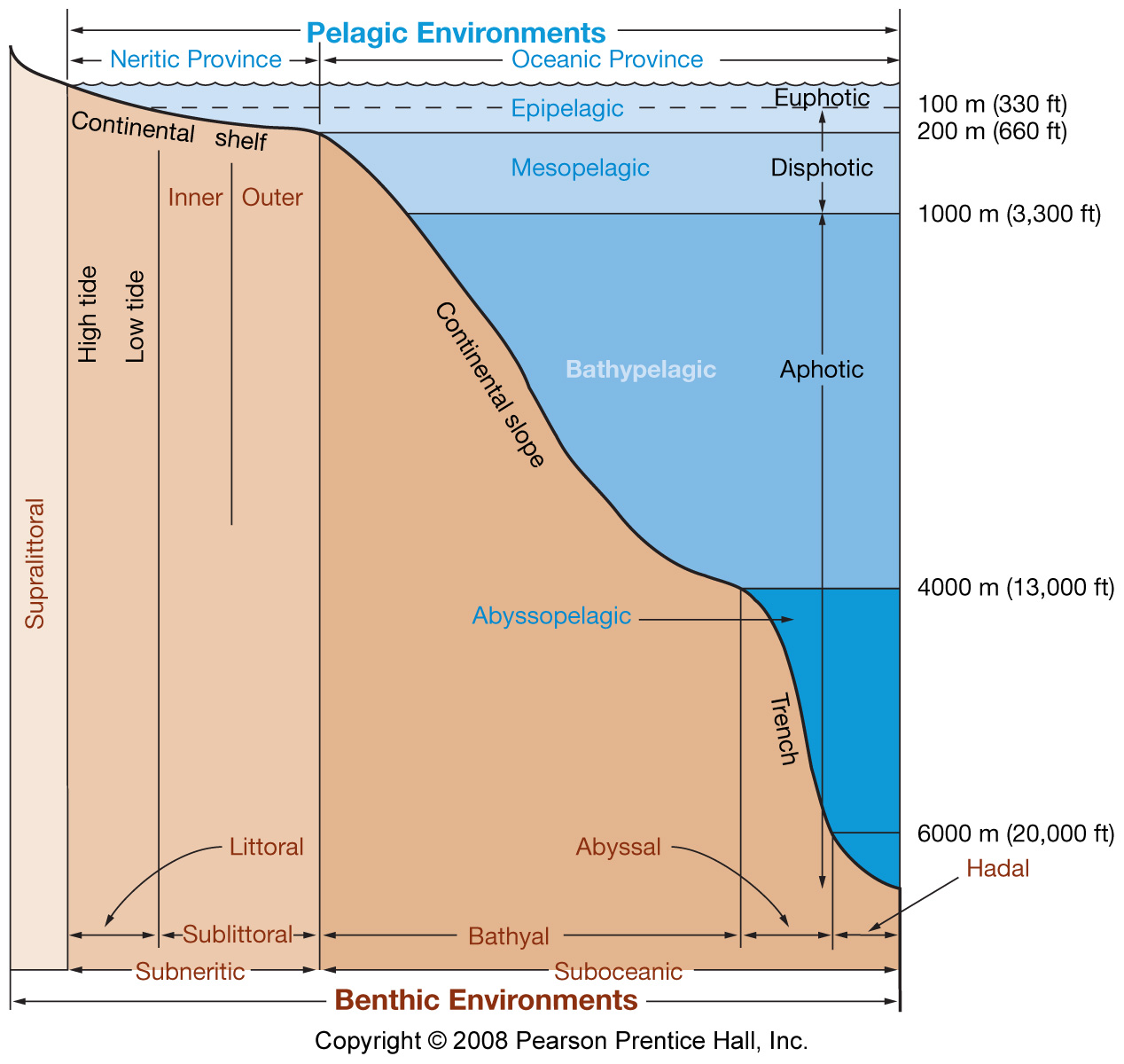
Marine life zones
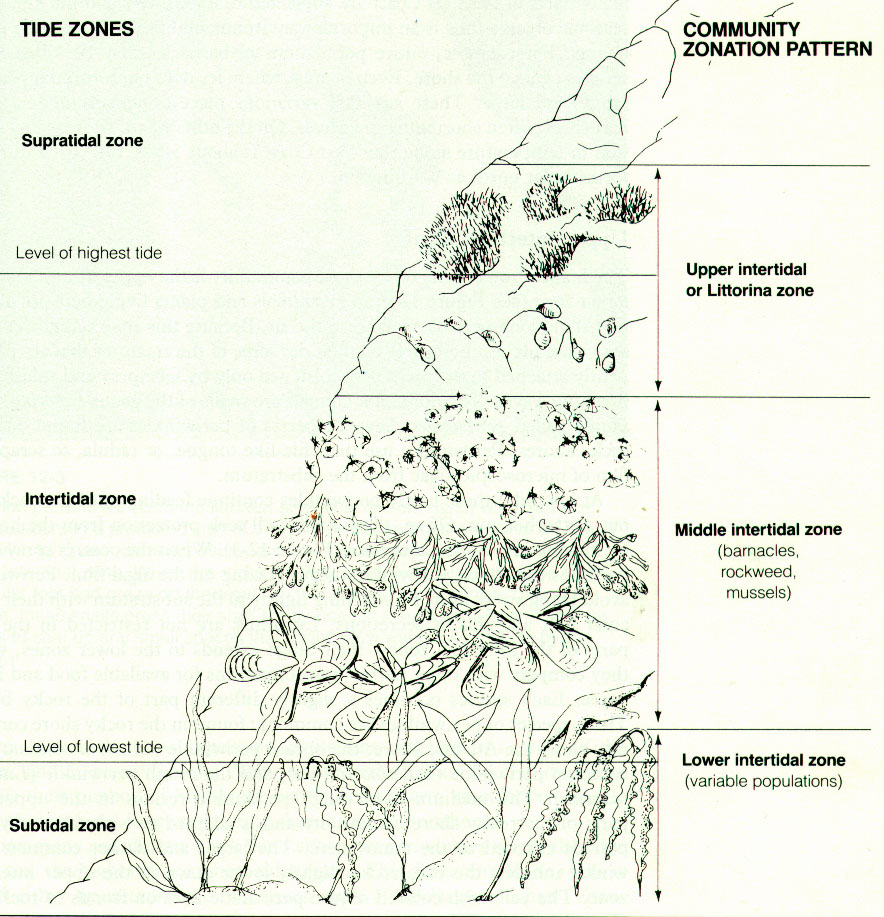
- Intertidal environment
- Supratidal zone
- Intertidal zone
- Subtidal zone
- Pelagic environment
- Neritic province
- Oceanic province
- Benthic environment
Intertidal environment
Pelagic environment
Benthic environment
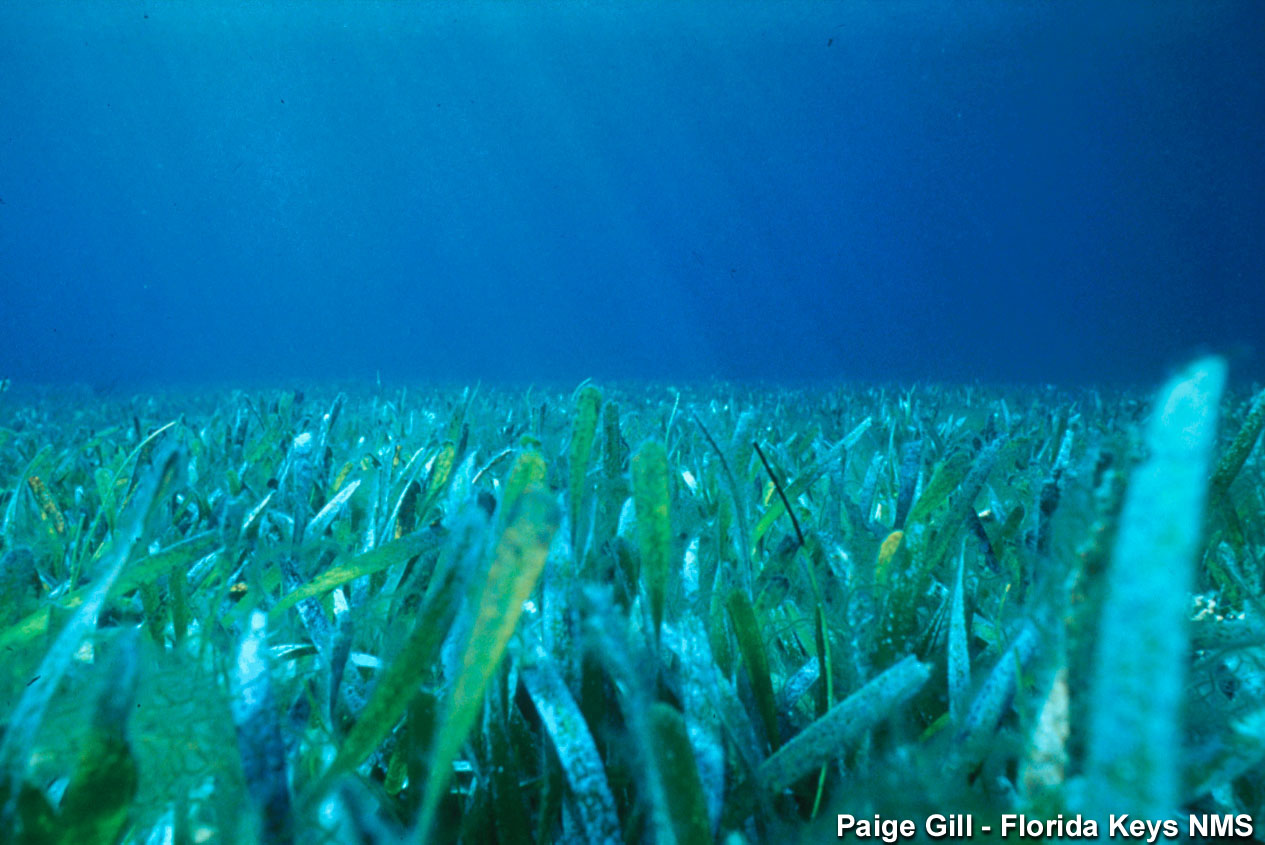
- Seagrass bed -- less than 10 m, high primary productivity, food and habitat source
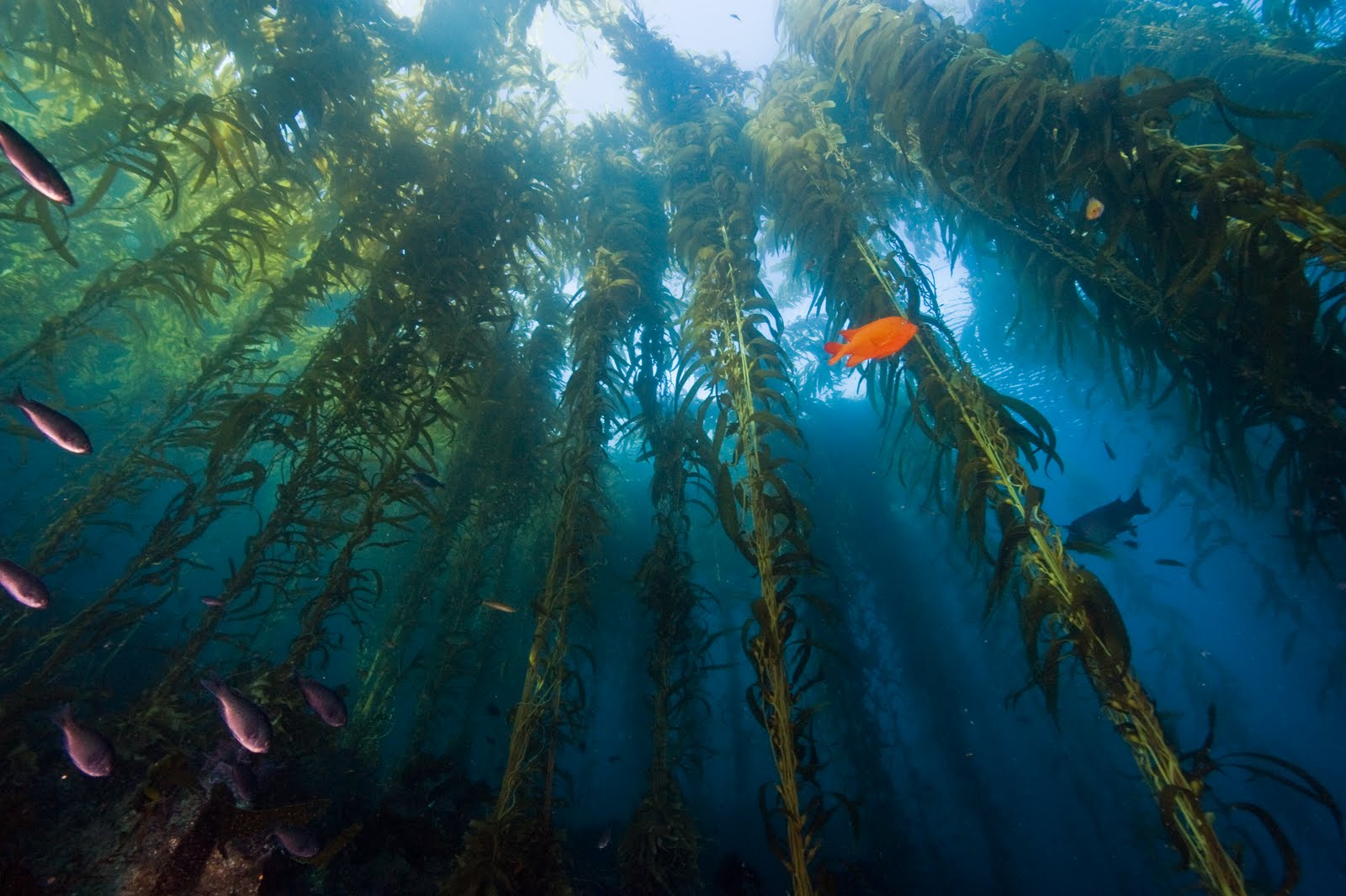
- Kelp forest -- approximately 25 m along rocky shorelines, habitat and indirect food source (through decomposition)
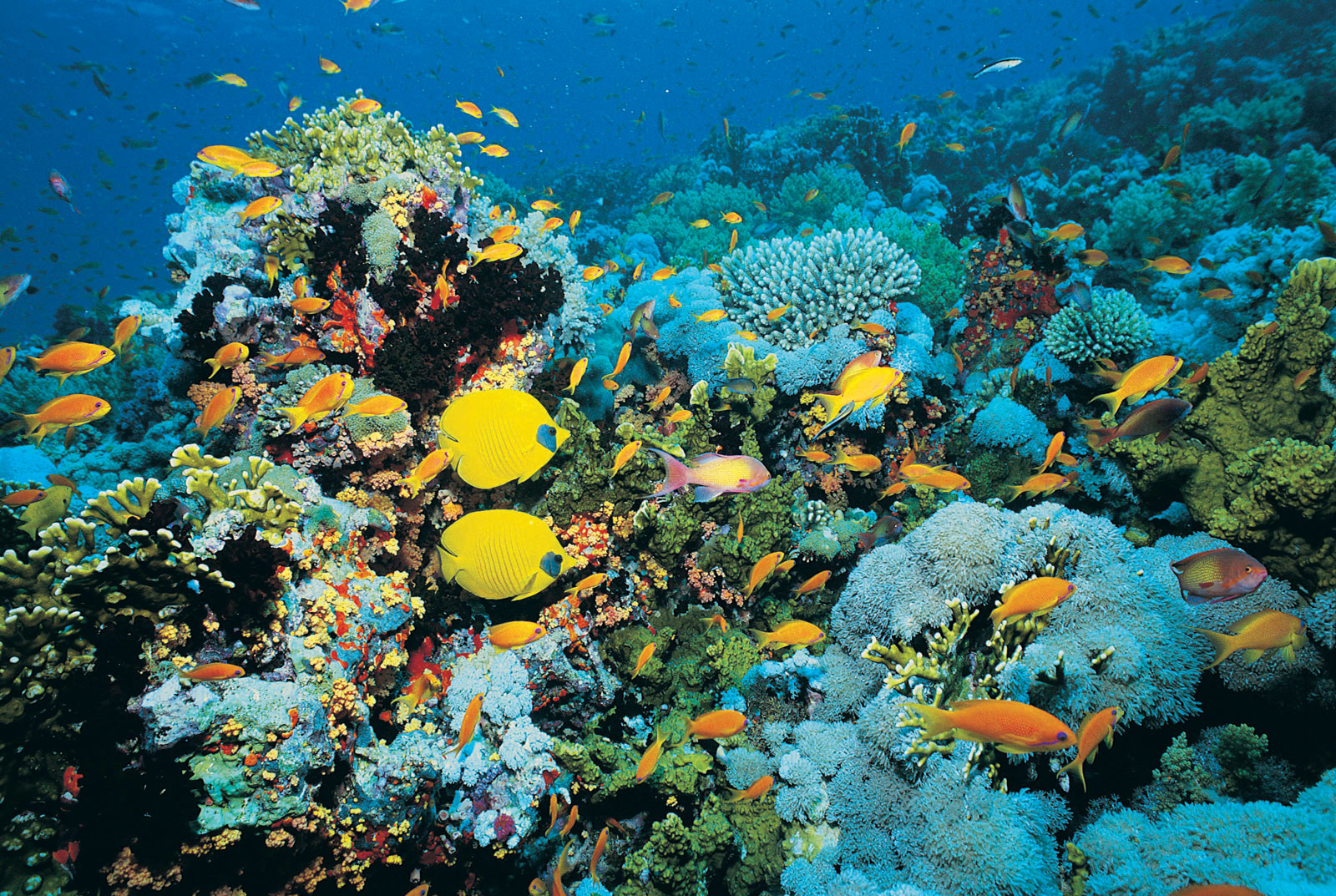
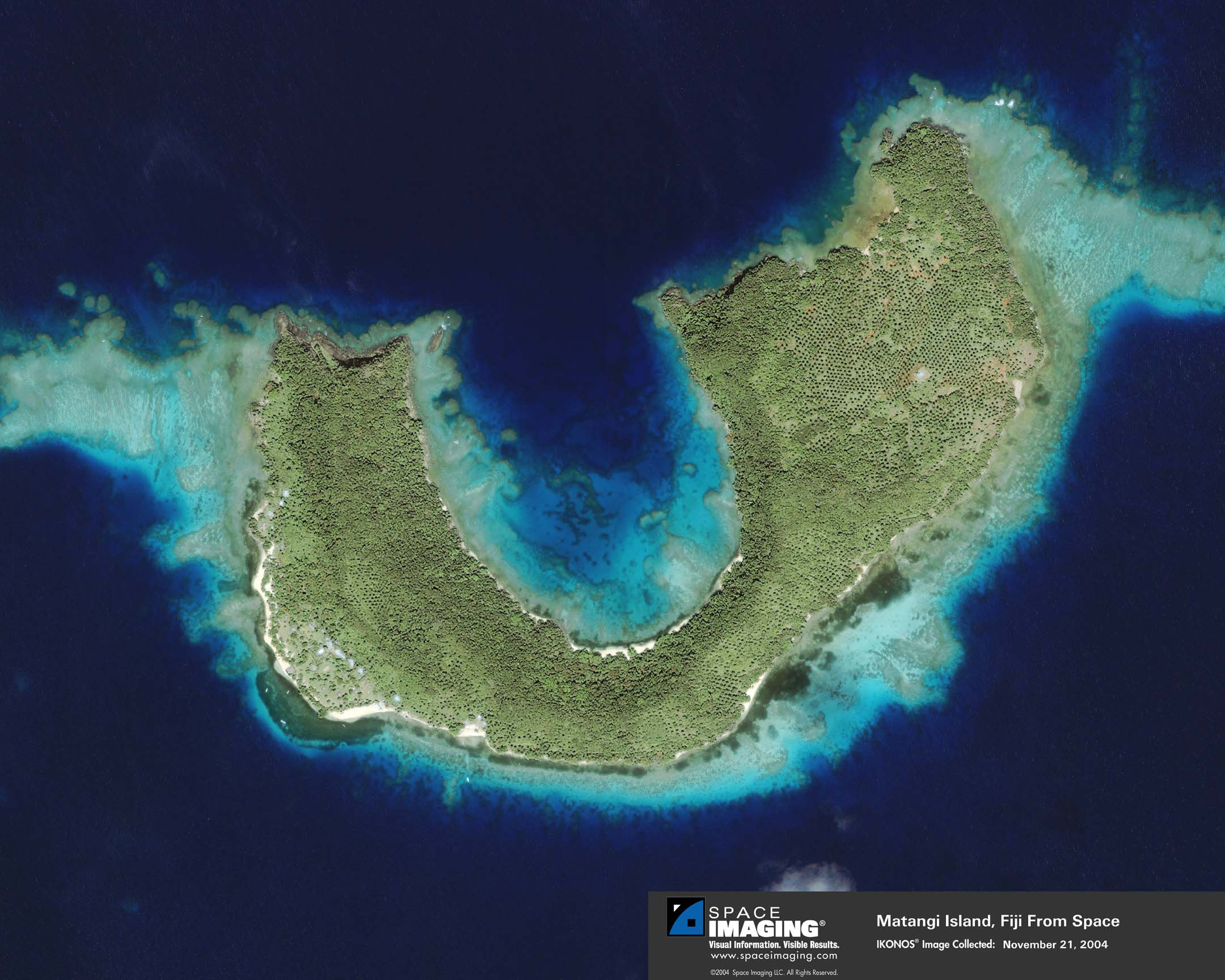
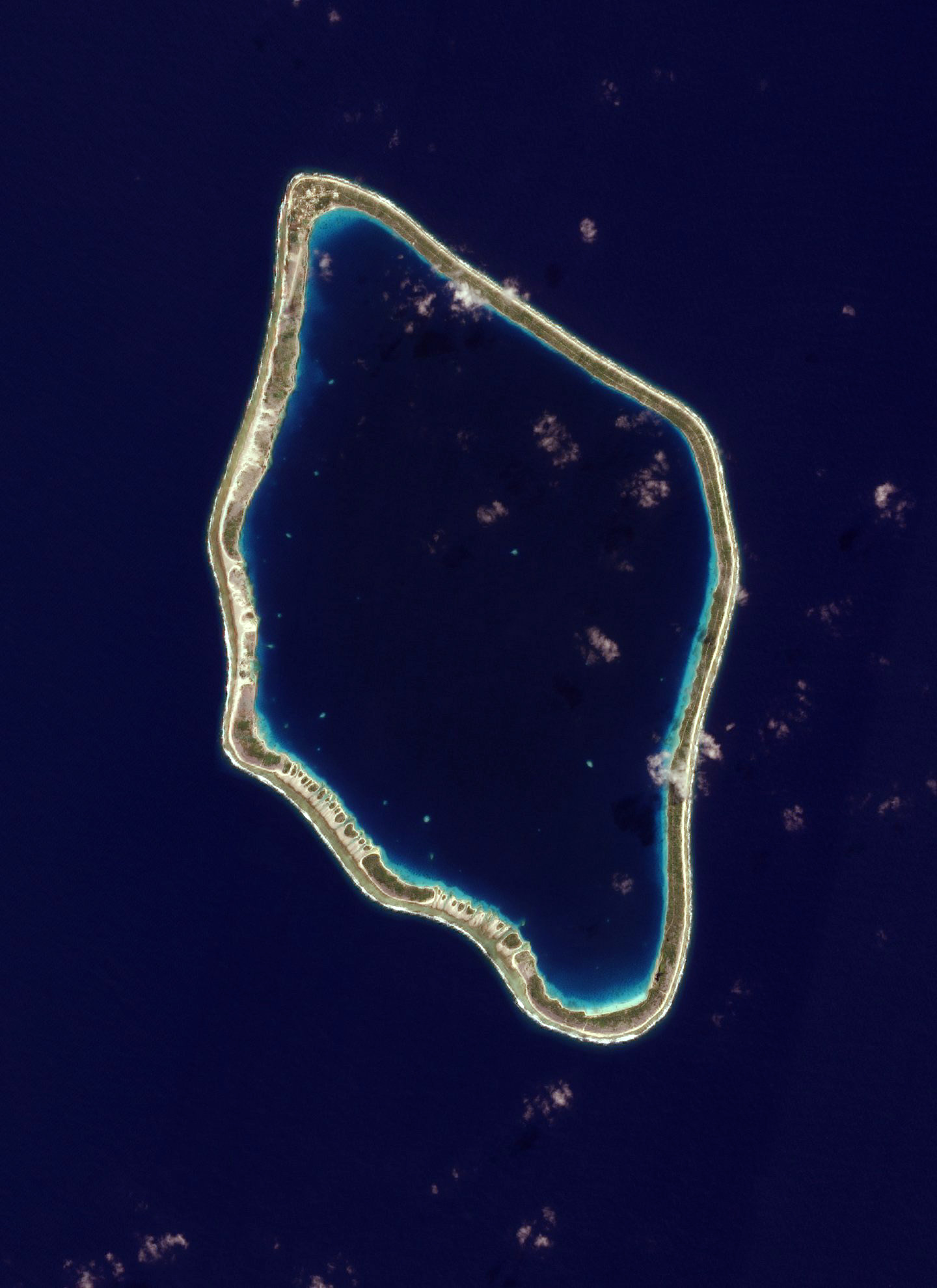
- Coral reef -- warm, shallow water with year-round sunlight (cold-water reefs also exist), water may be nutrient poor
- Fringing reef
- Atoll
- Barrier reef
Seagrass bed
Kelp forest
Coral reef
Fringing reef
Atoll
Barrier reef
Threats to the ocean
- Non-point-source pollution
- Point-source pollution
- Invasive-alien species
- Overharvesting
- Bycatch
- Aquaculture
- Coastal development
- Habitat destruction
- Climate change
Brian M Napoletano
2011-09-21