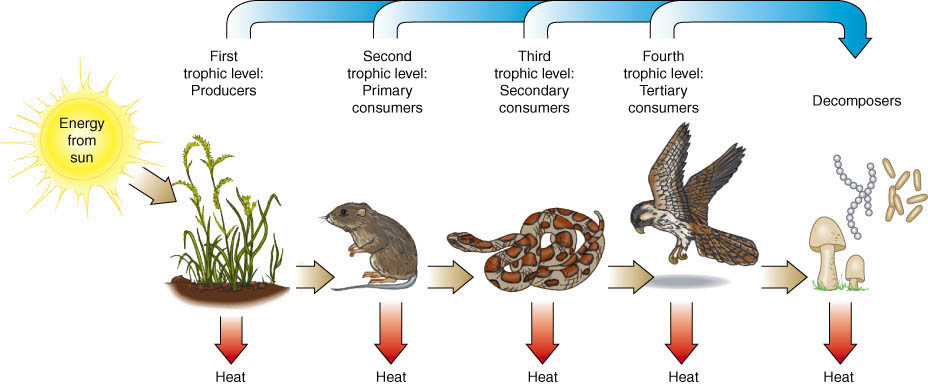
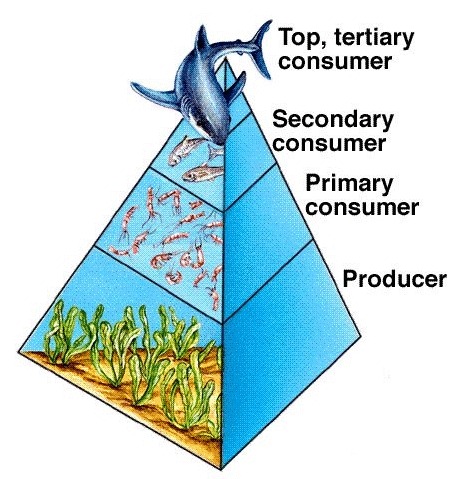
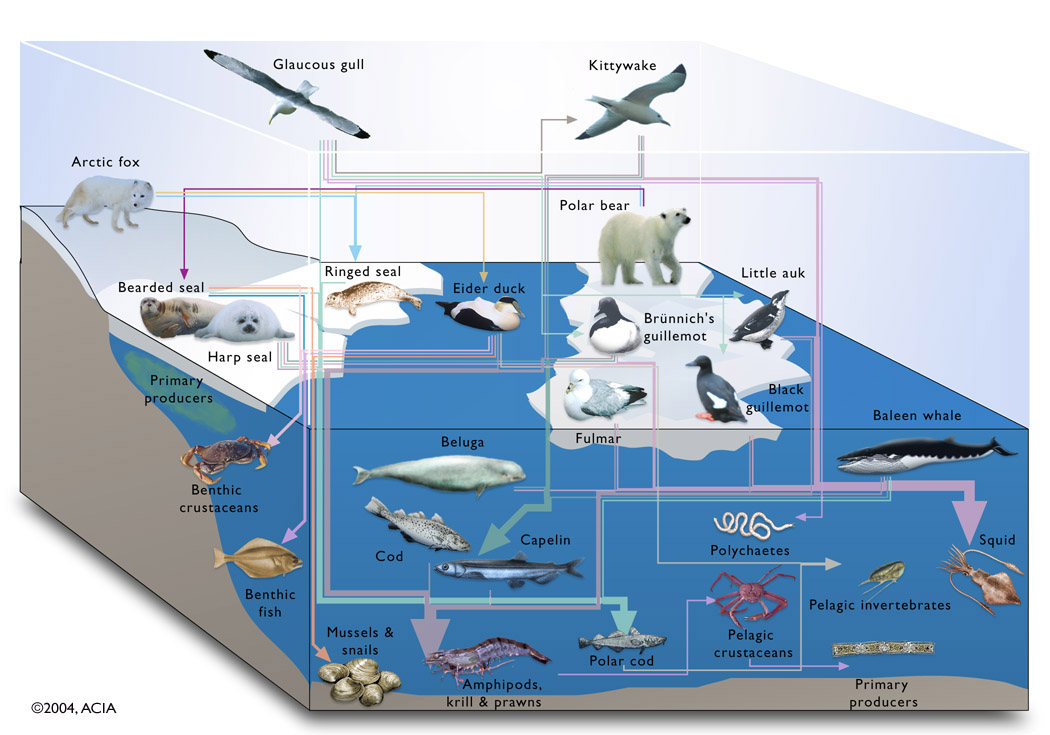
Basic Food Chain
Basic Food Pyramid
Producers
- Also called autotrophs (as opposed to heterotrophs)
- Convert inorganic matter into organic molecules
- Plants, algae, and some bacteria
Primary Consumers
- Consume producers
- Herbivores
- Convert plant material into usable substances
Secondary Consumers
- Consume primary consumers
- Carnivores
- Cannot convert plant material
Tertiary Consumers
- Consume secondary consumers (although many may also consume primary consumers)
- Also carnivores
- ``Top predators''
- Cannot convert plant material
- Least efficient in terms of energy flow
Omnivores
- Both primary and secondary/tertiary consumers
- Can convert plant material
- Some can be consumed by tertiary consumers
Detritivores
- Consume detritus (i.e. inert organic matter)
- Can convert both plant and animal material
- Work in conjunction with decomposers
Decomposers
- Saprotrophs (and heterotrophs)
- Break down inert organic matter into forms that can be used again by producers
- Work in conjunction with (and are sometimes the same as) detritivores
Food Web
- Most organisms rely on multiple food choices
- More complex model
- More realistic model
- Energy still constrained to move in one direction
- Energy is dissipated as heat at each juncture
Simplified Temperate Forest Food Web
Arctic Marine Food Web
Brian M Napoletano
2011-09-12